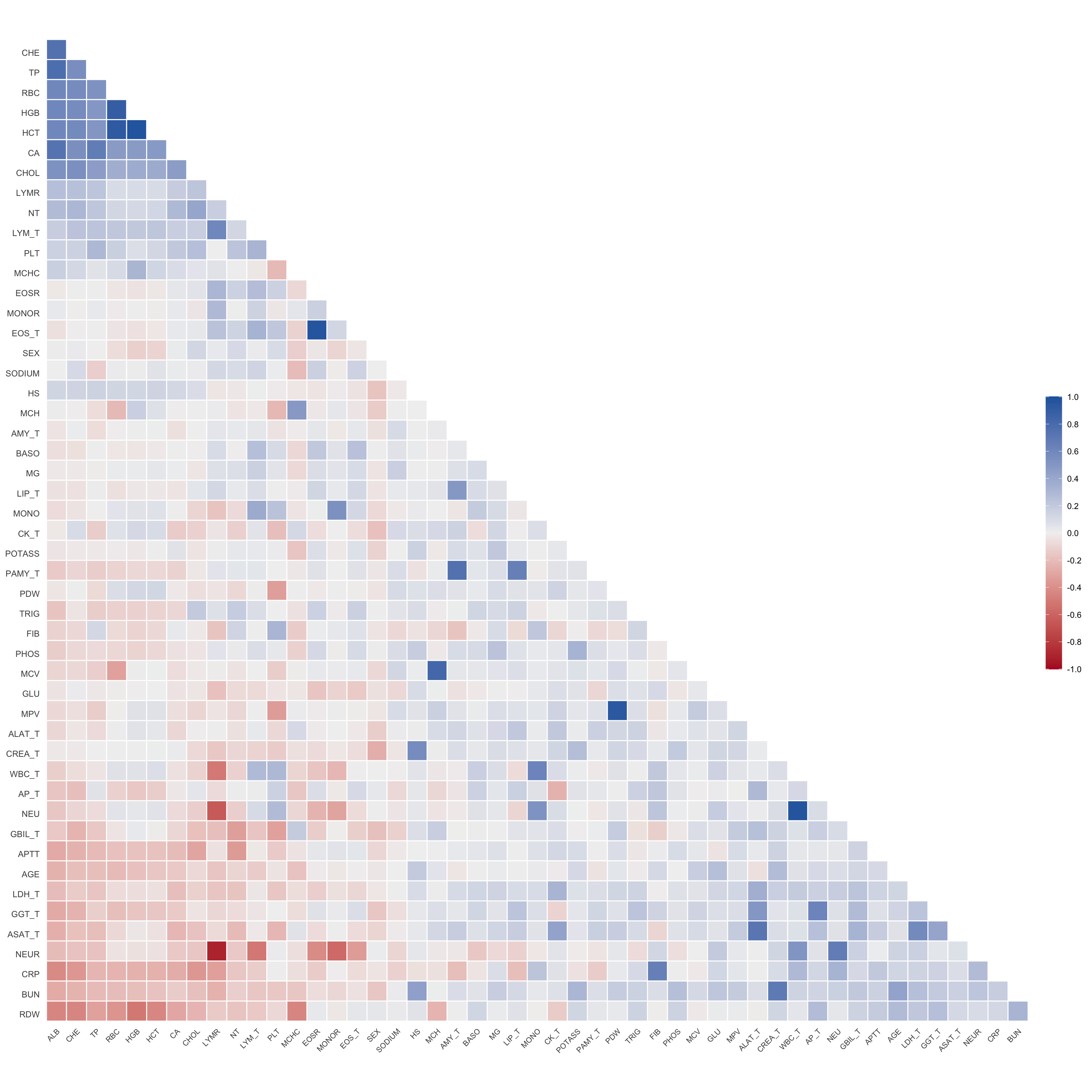
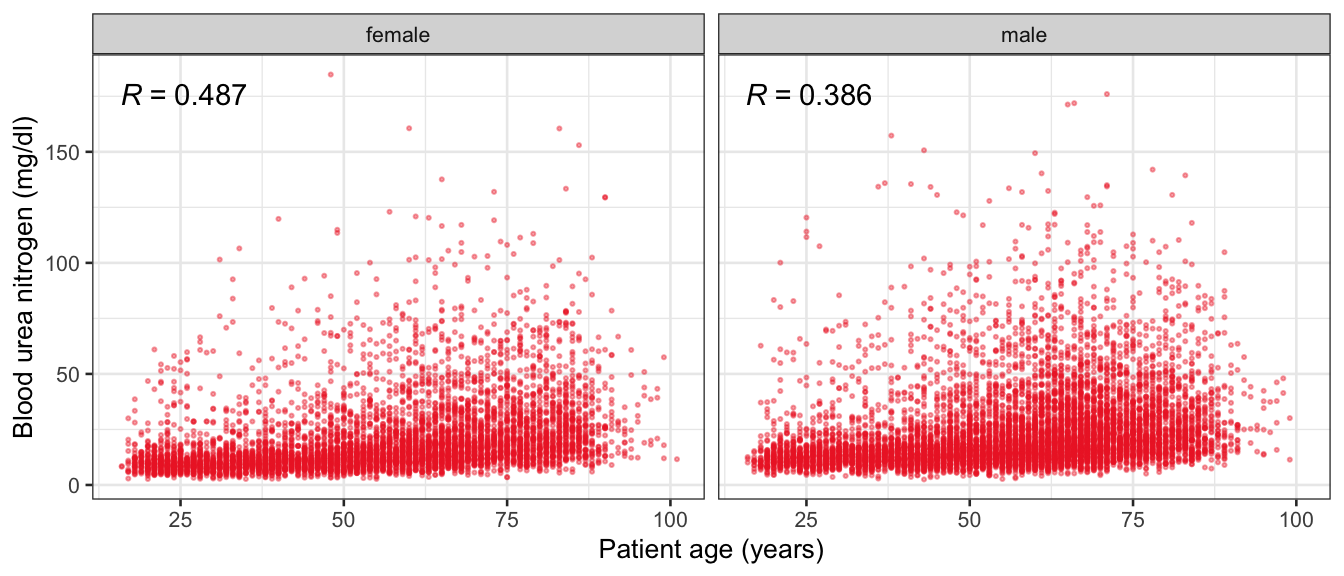
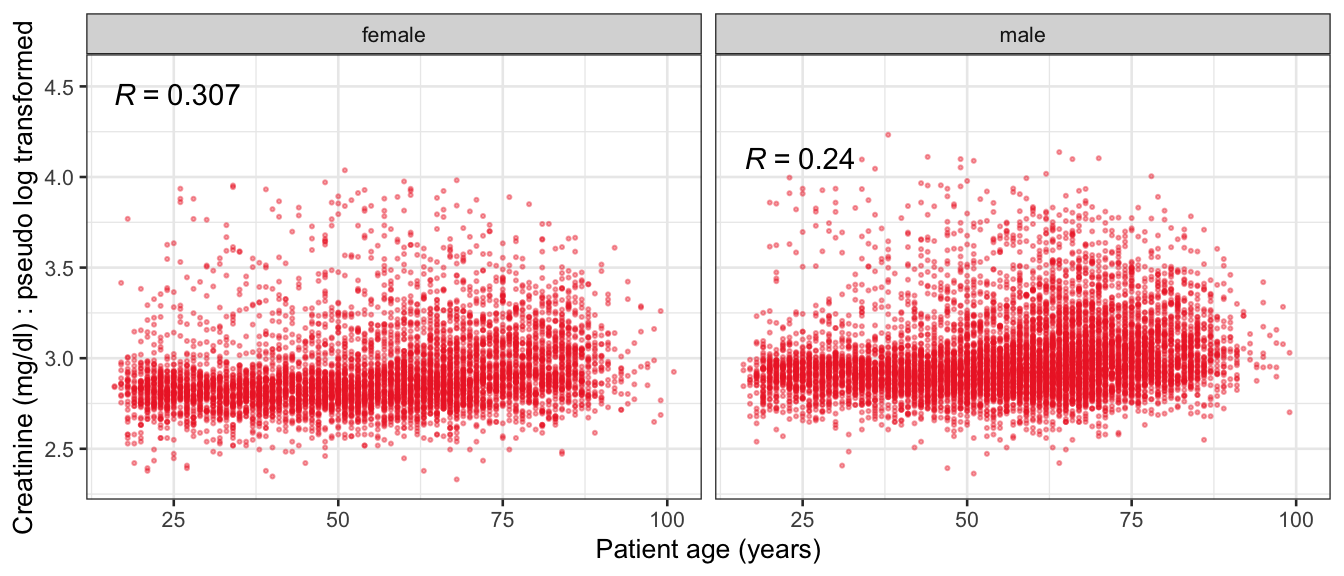
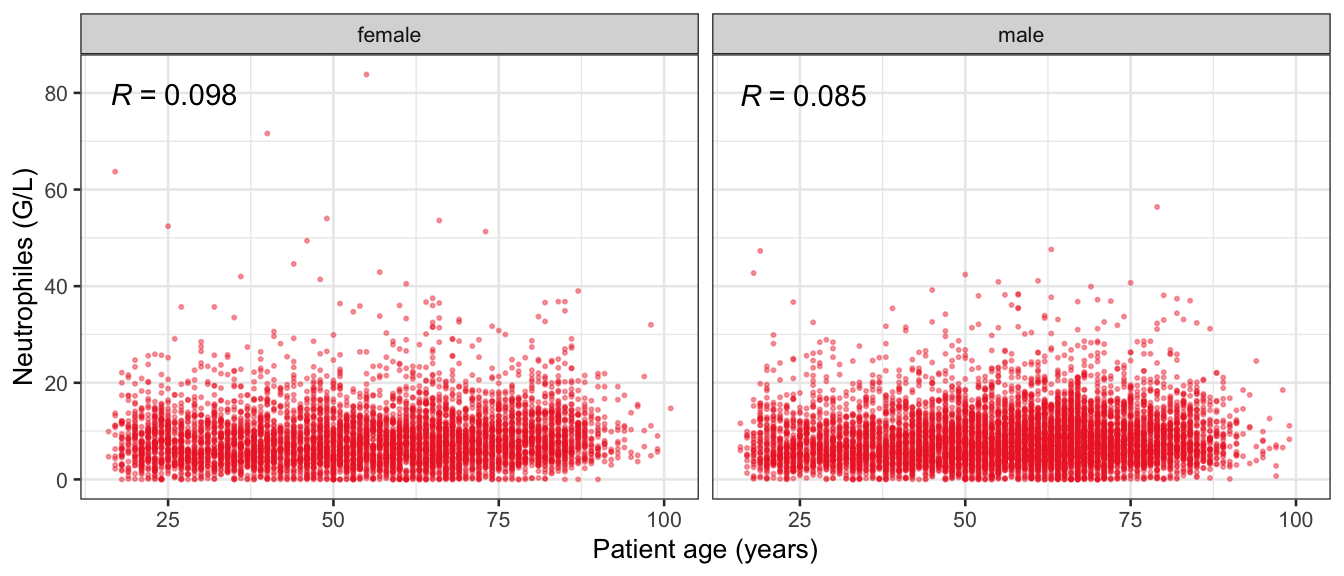
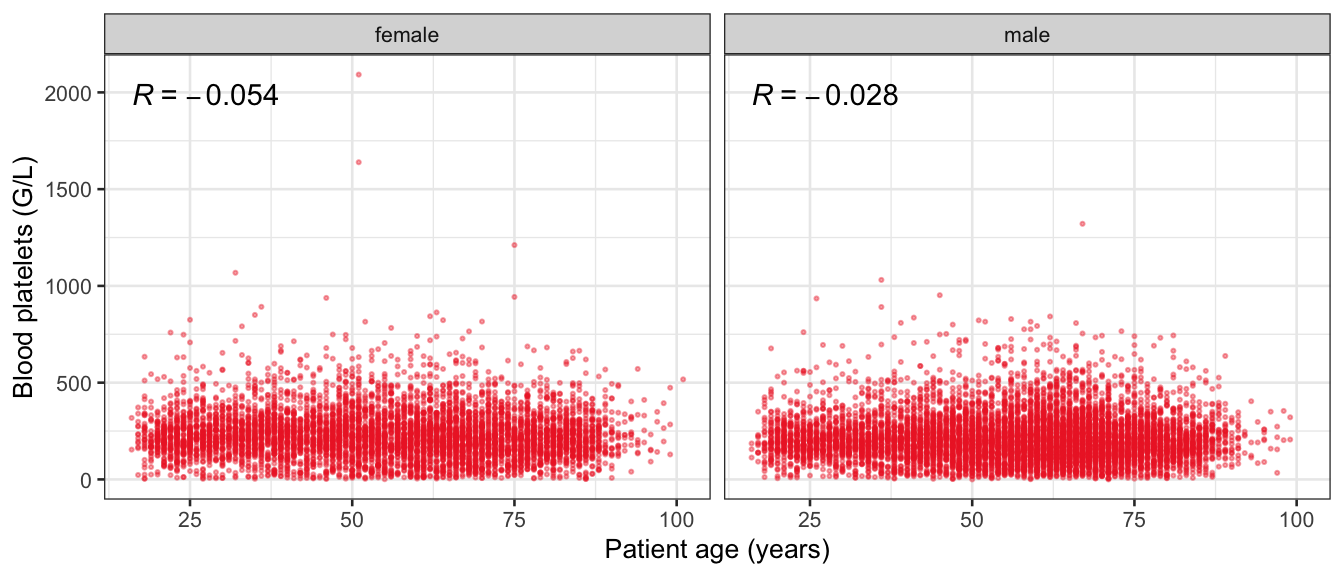
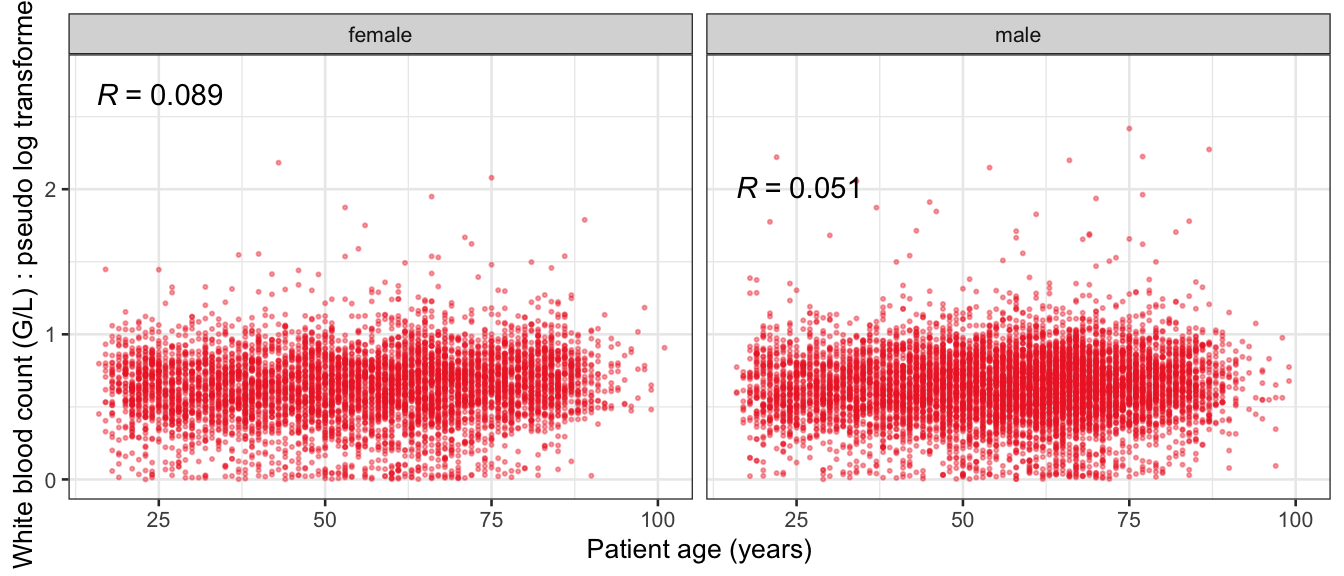
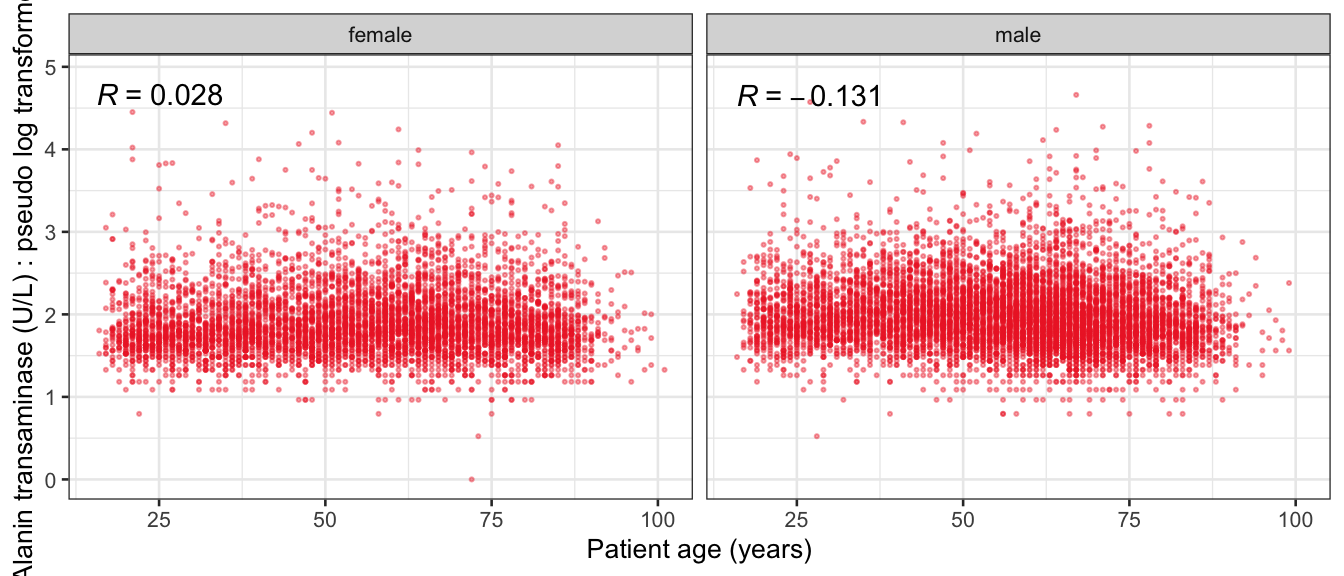
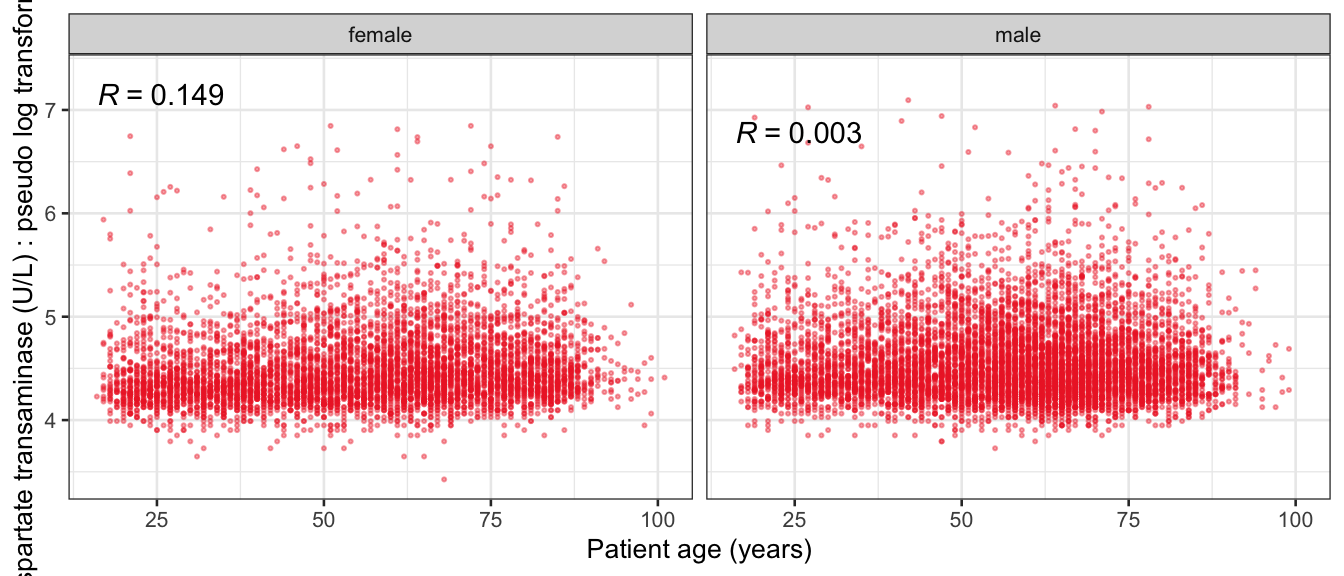
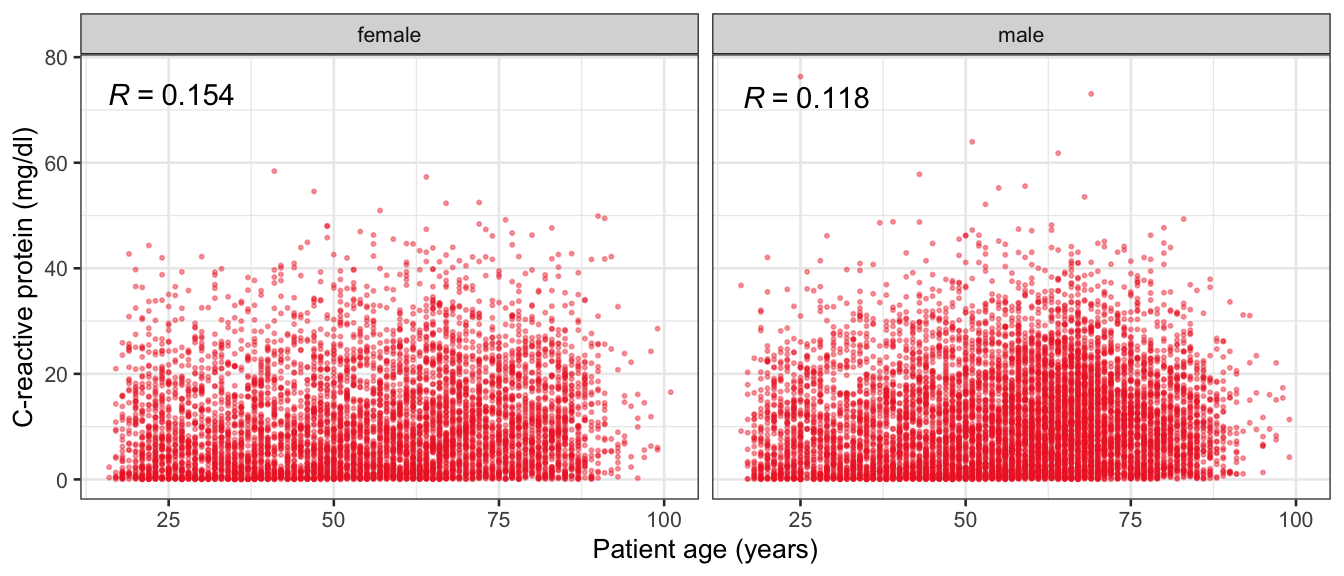
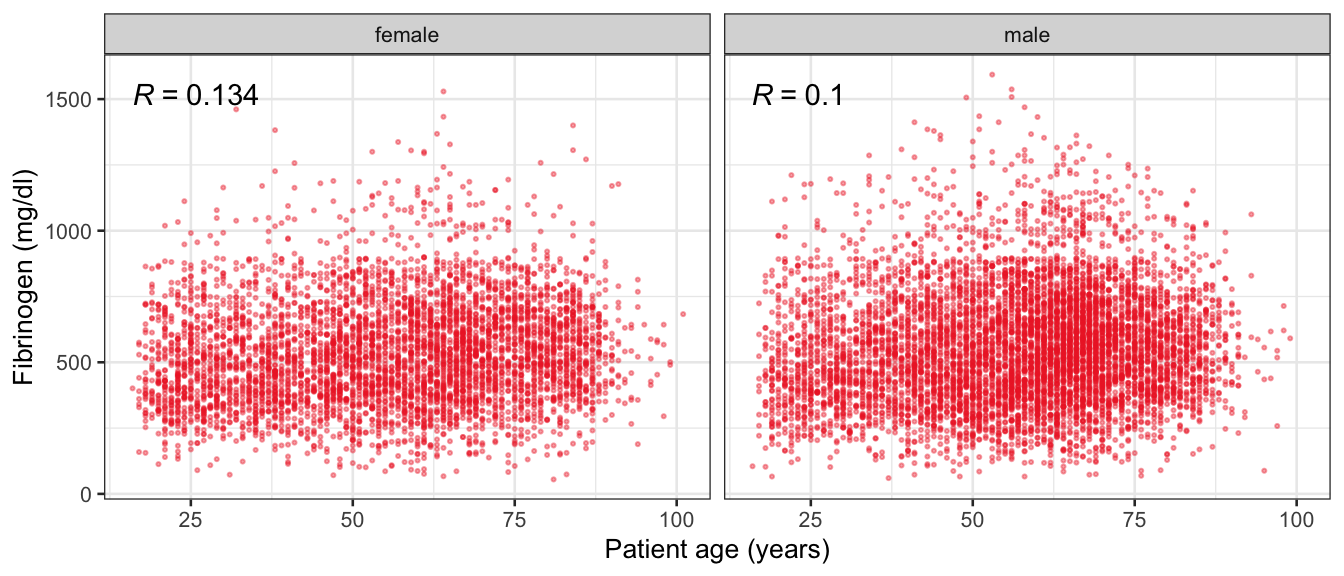
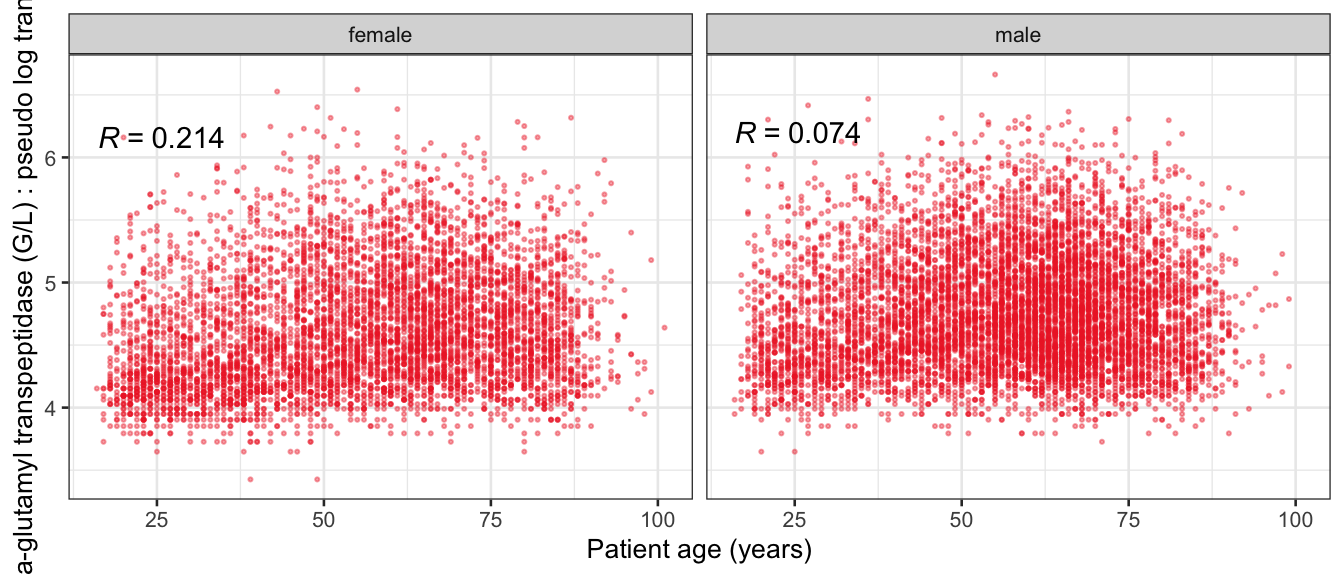
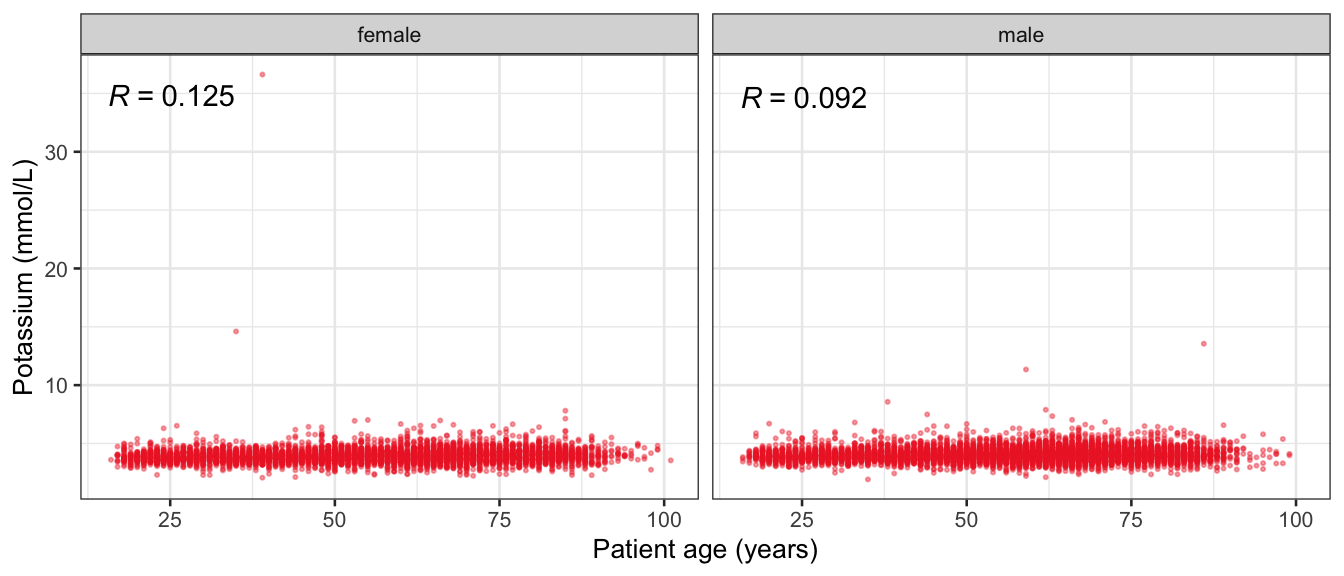
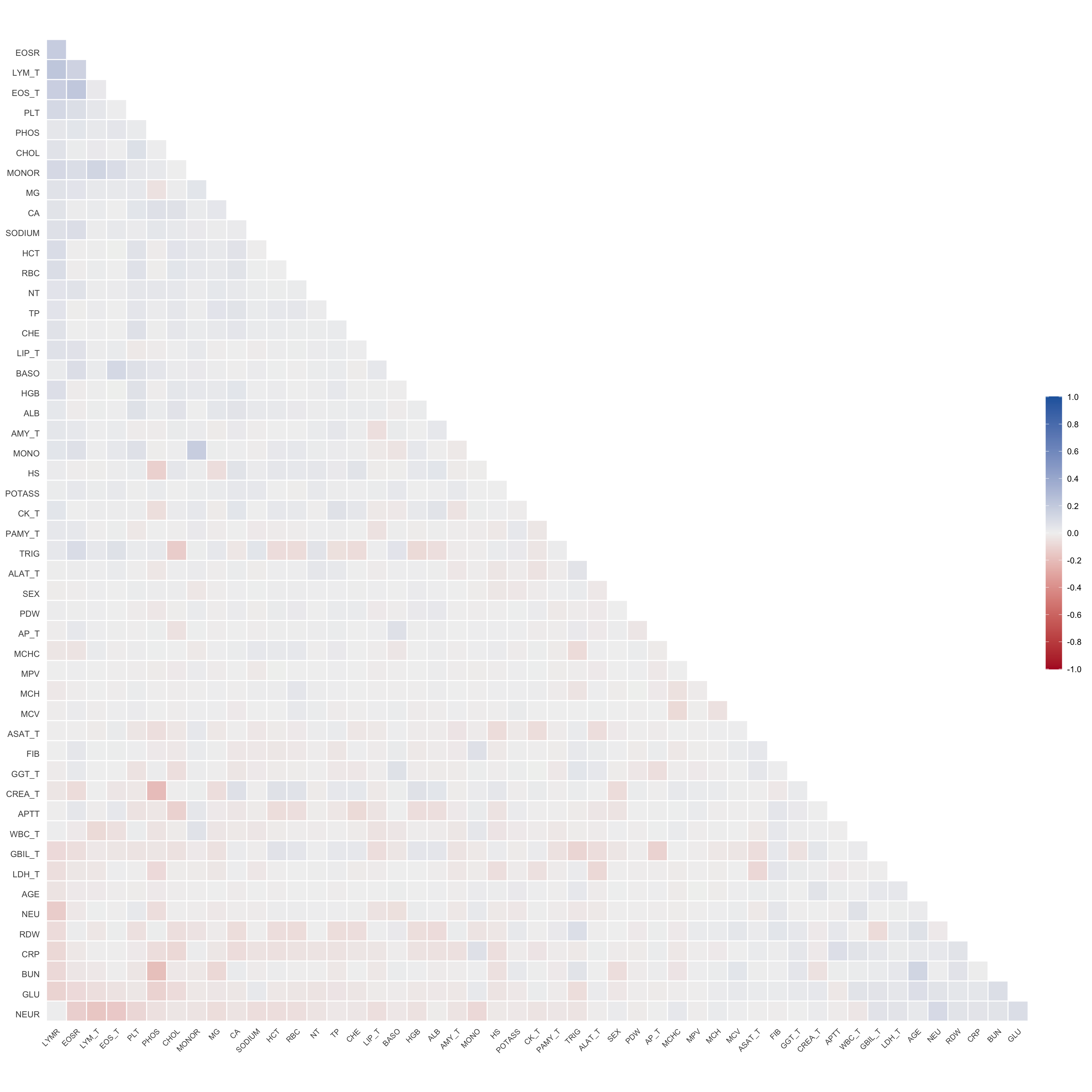
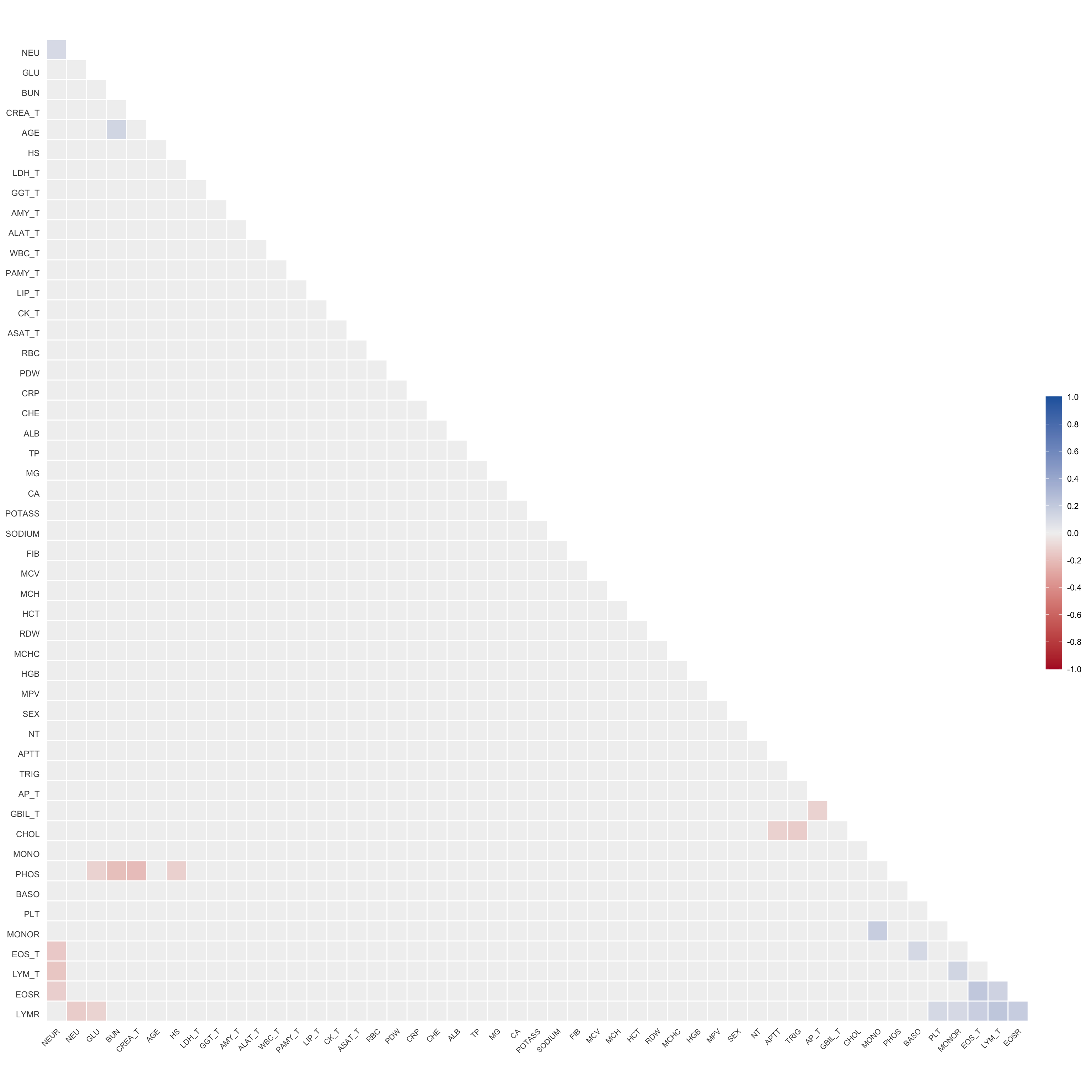
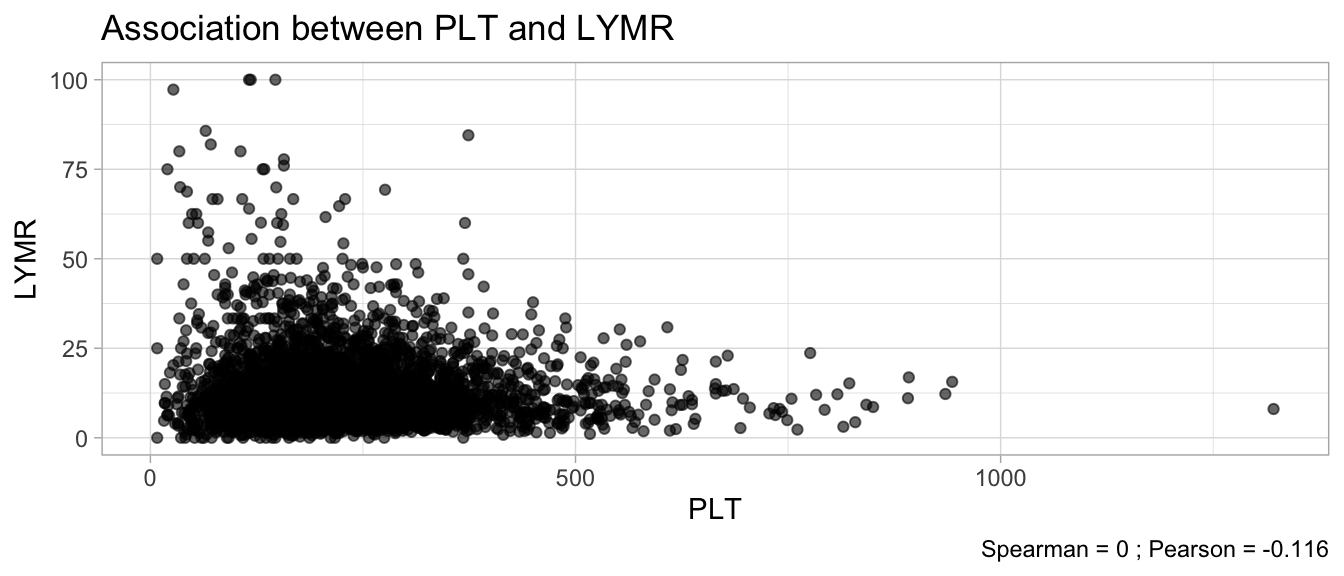
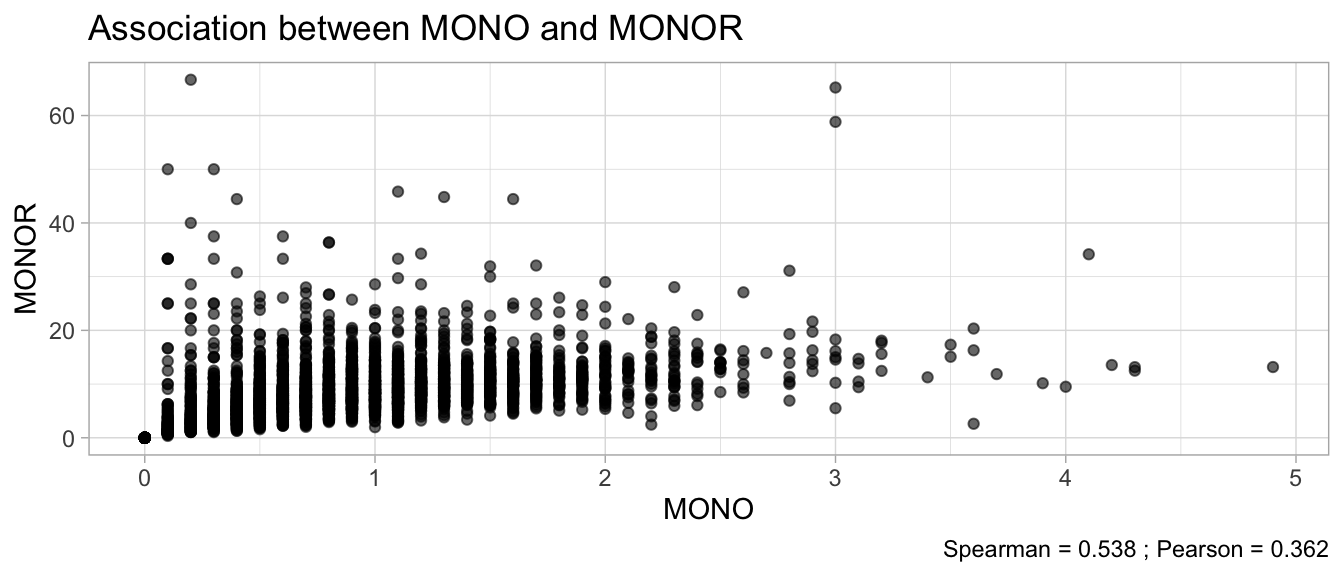
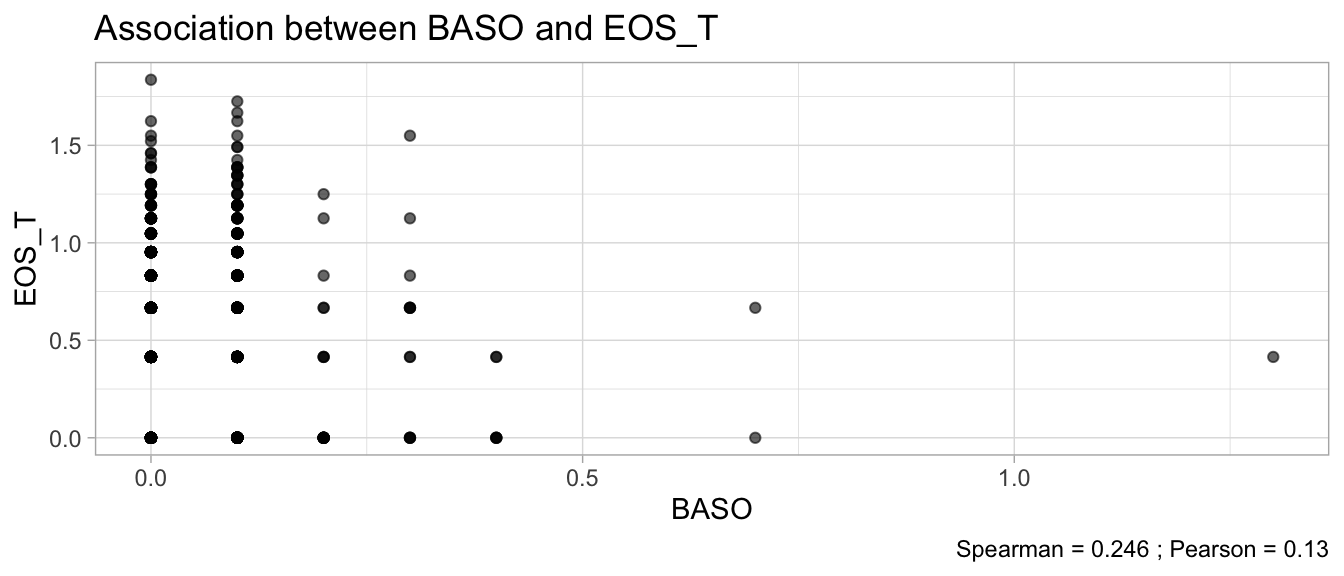
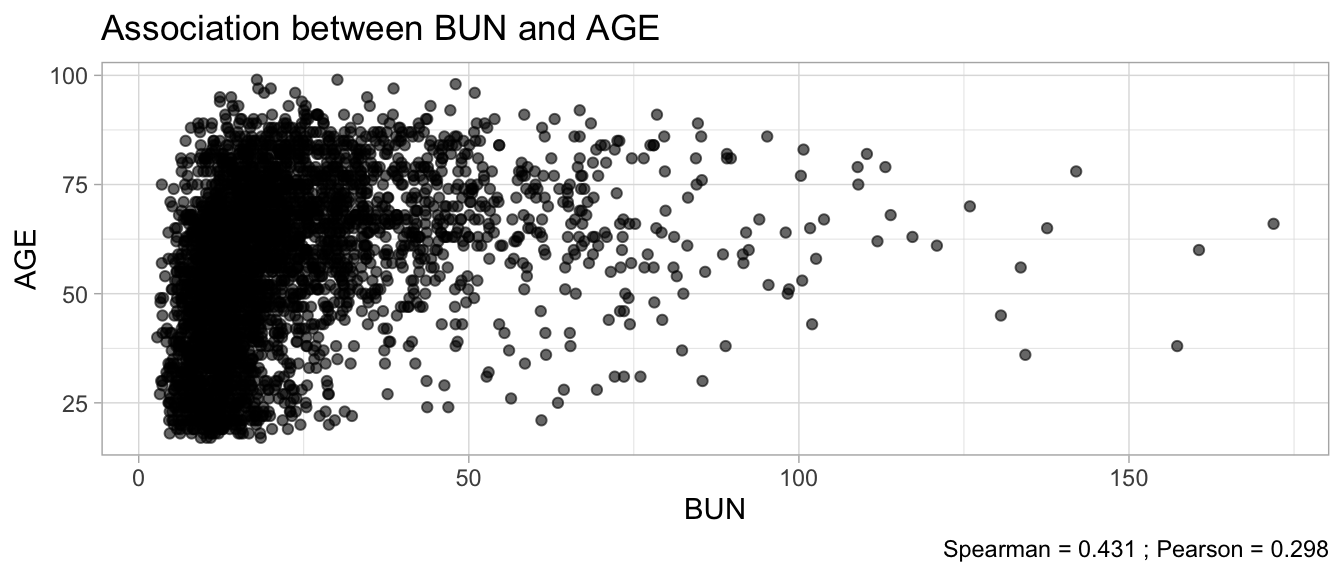
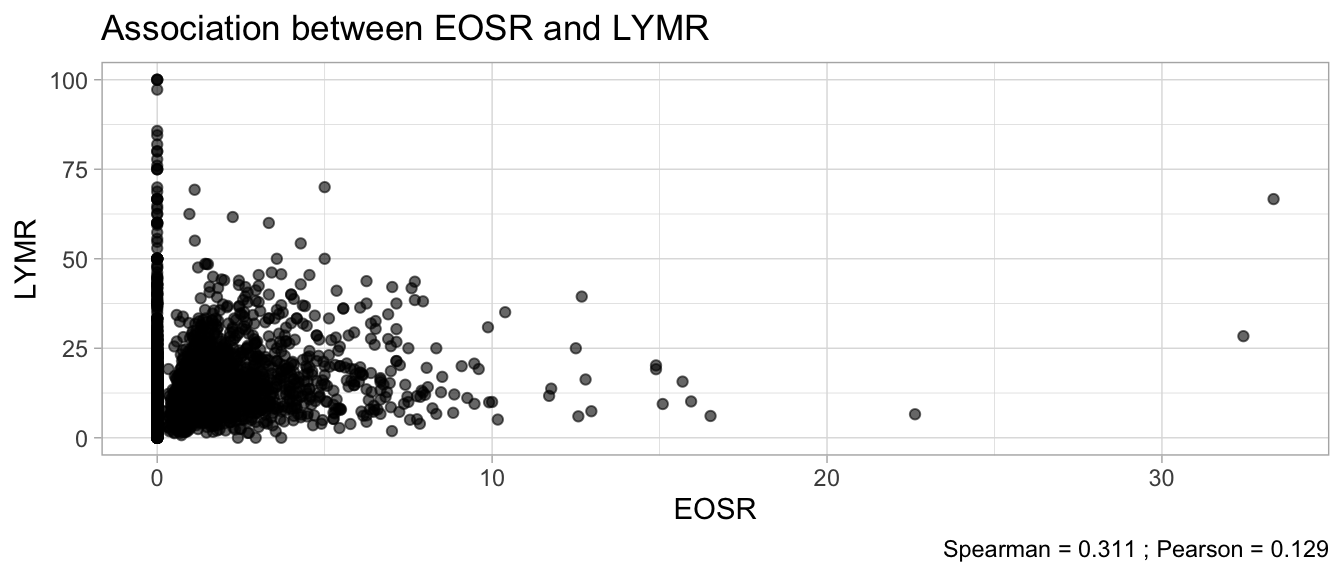
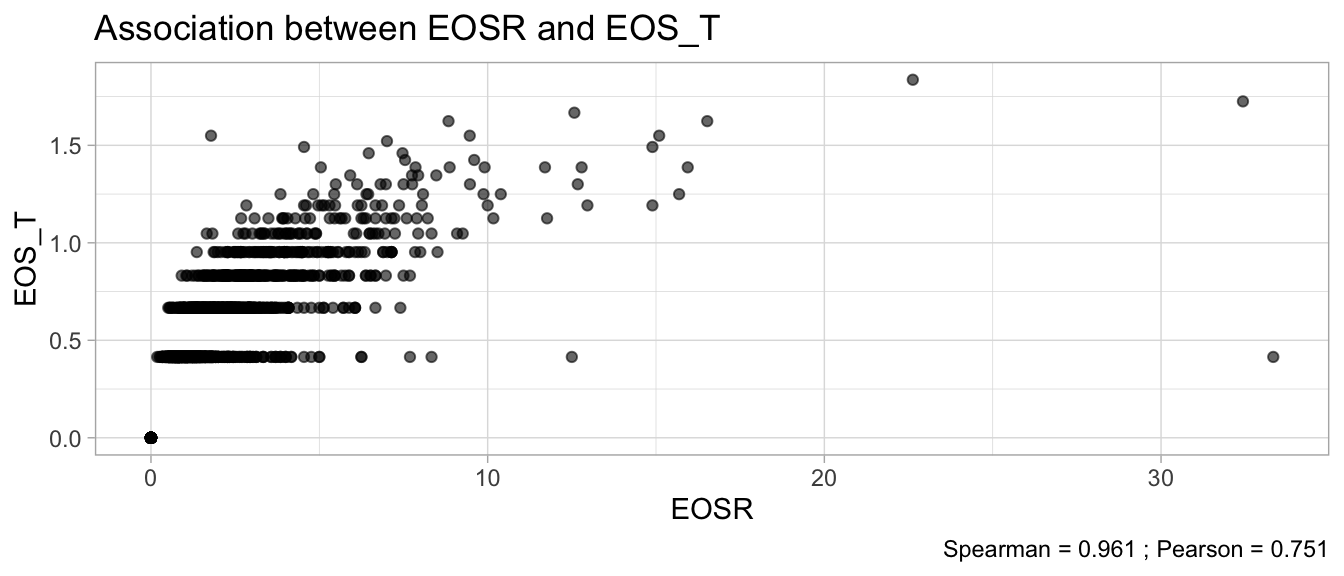
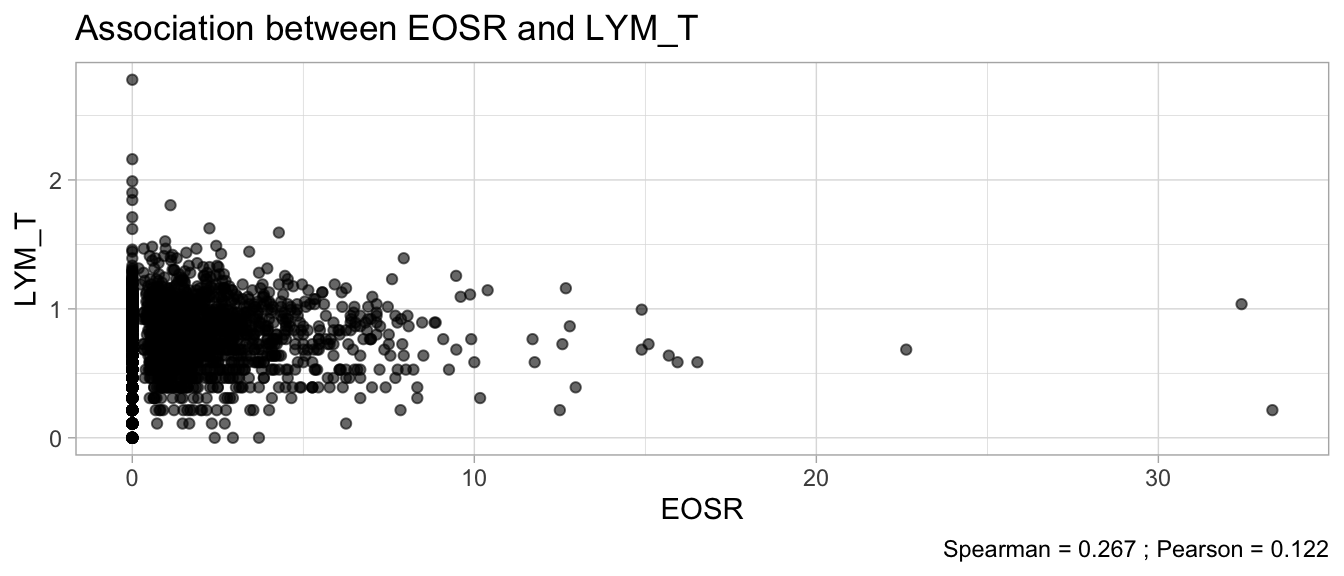
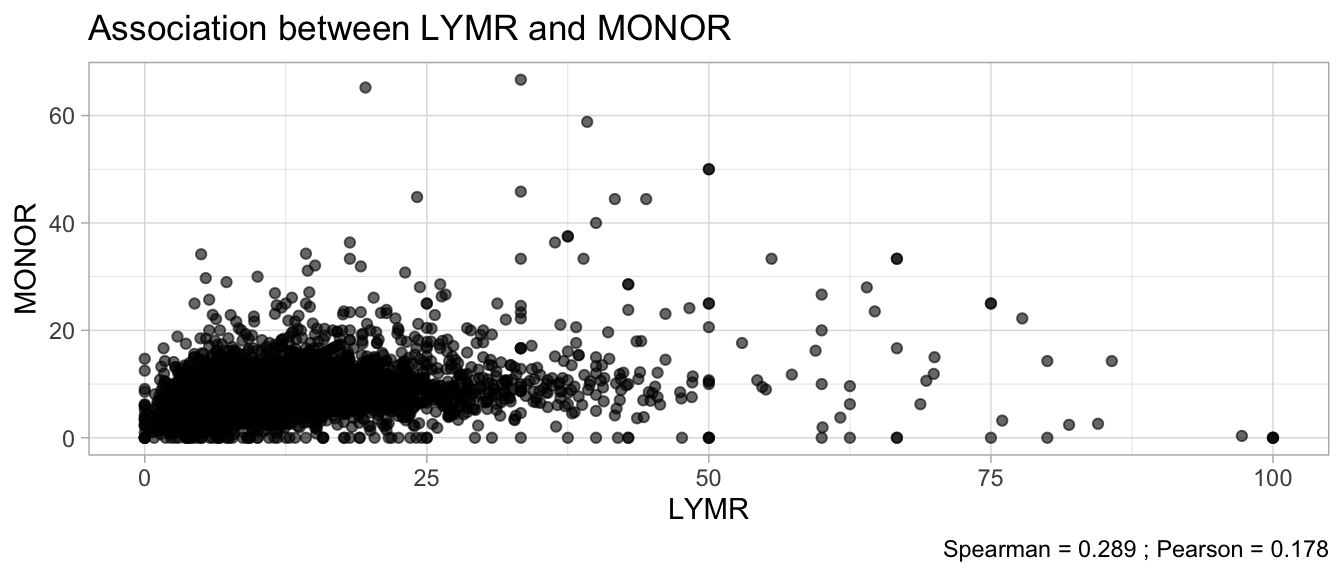
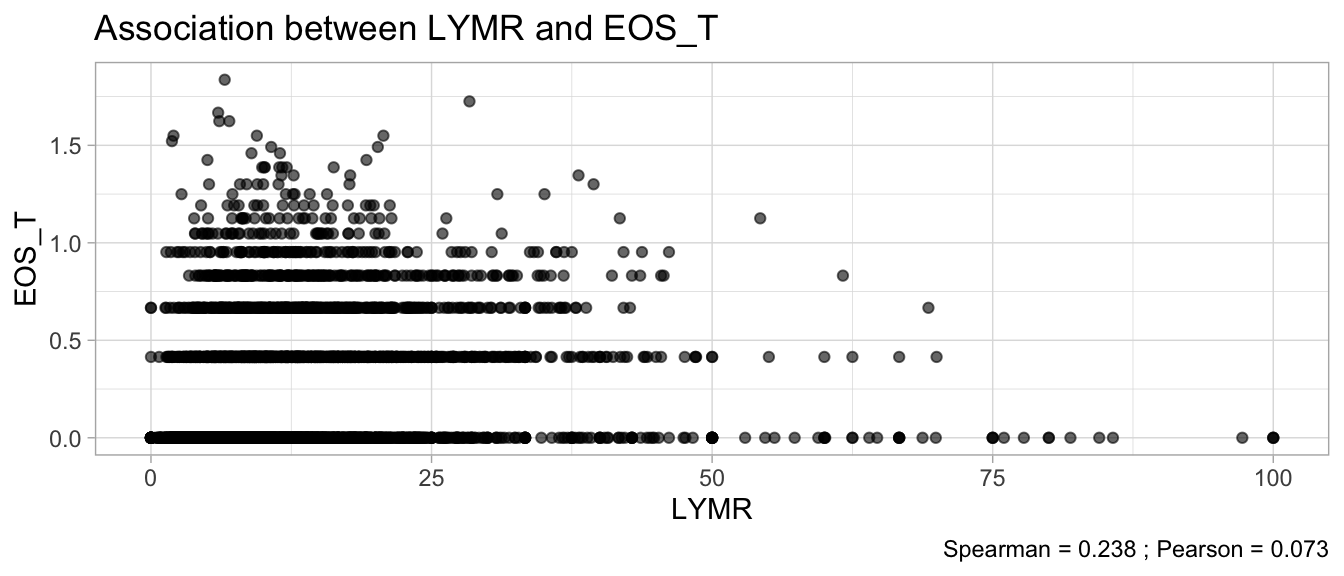
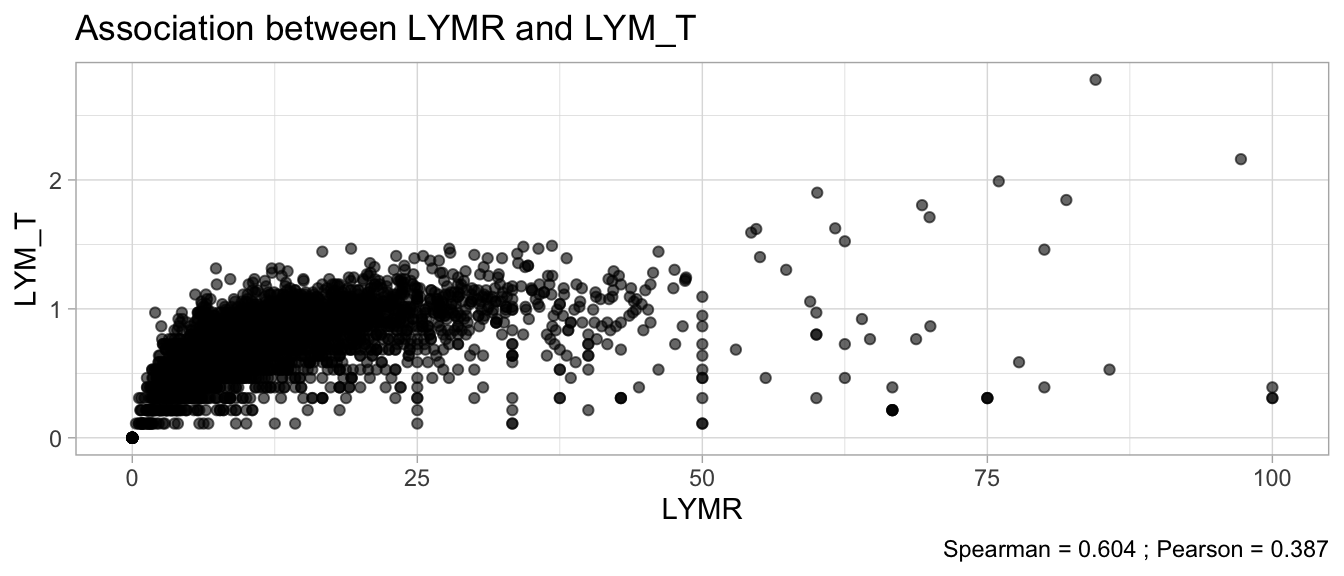
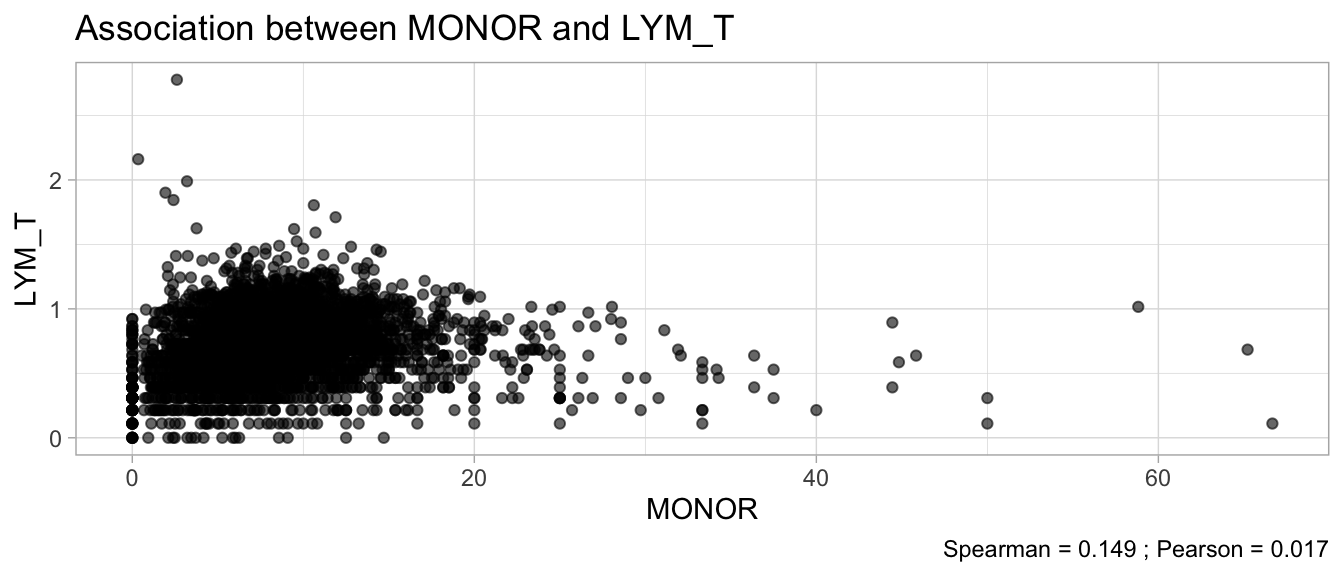
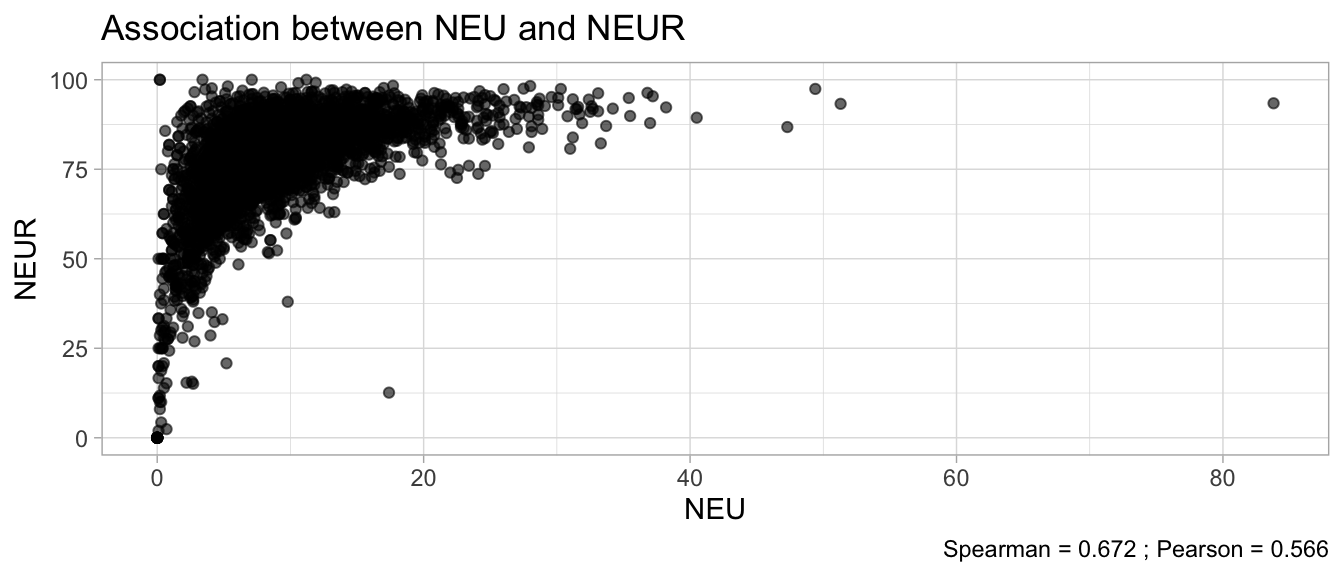
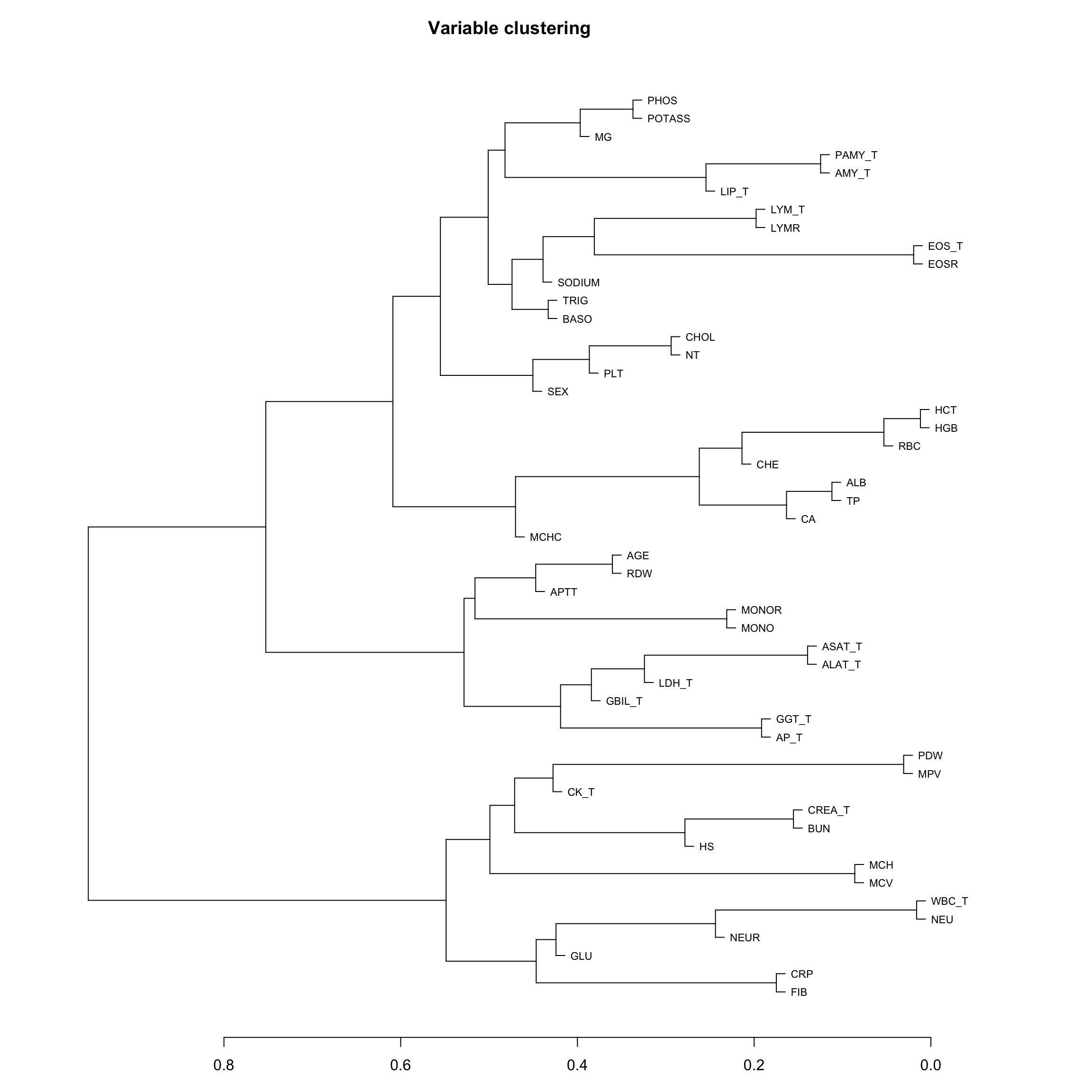
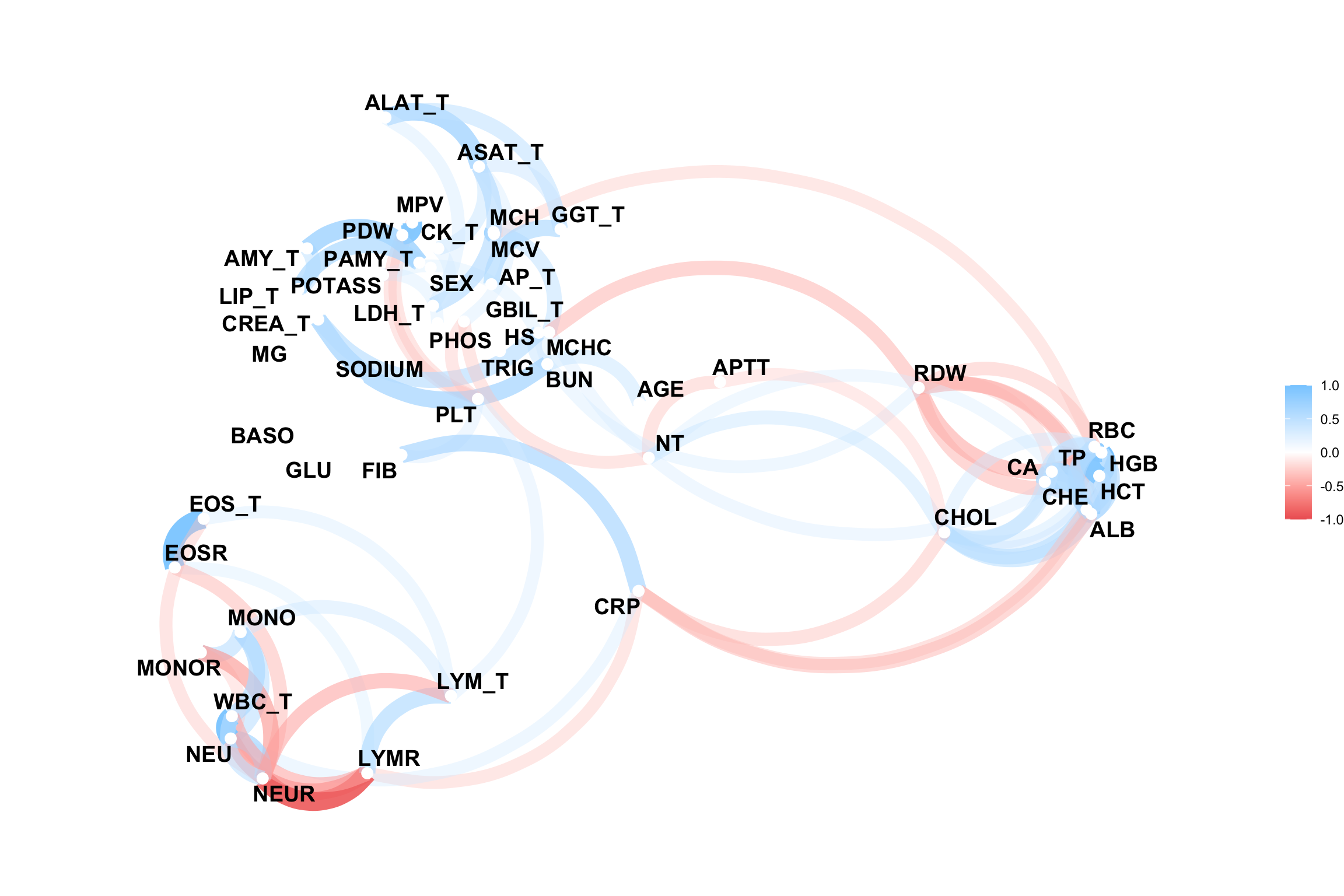
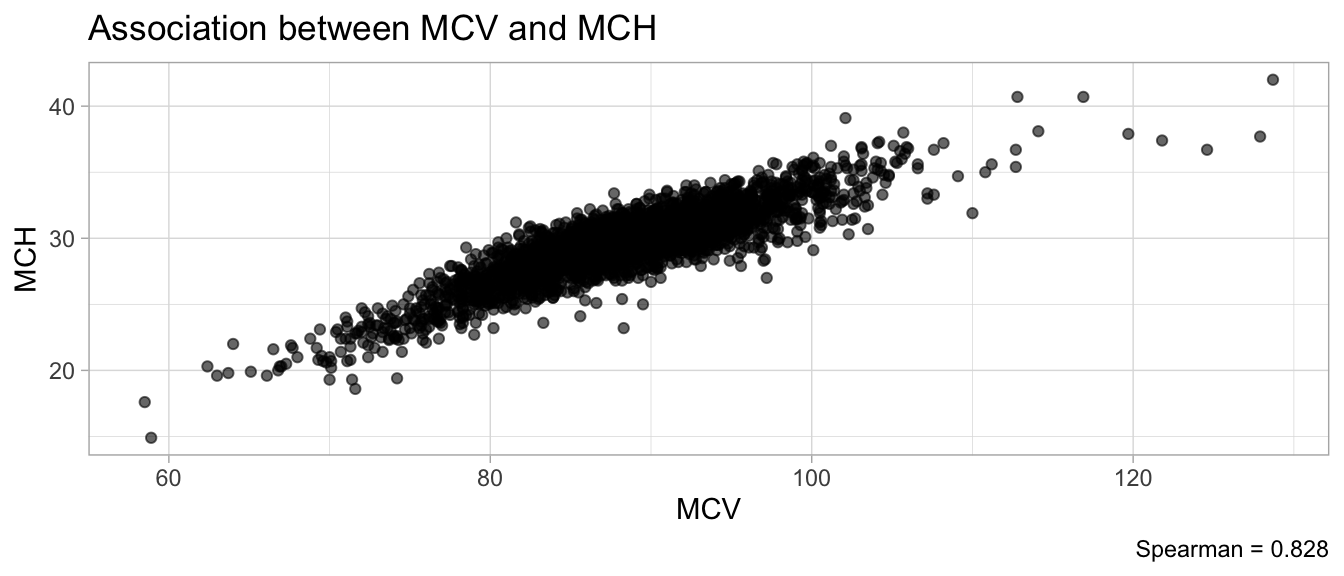
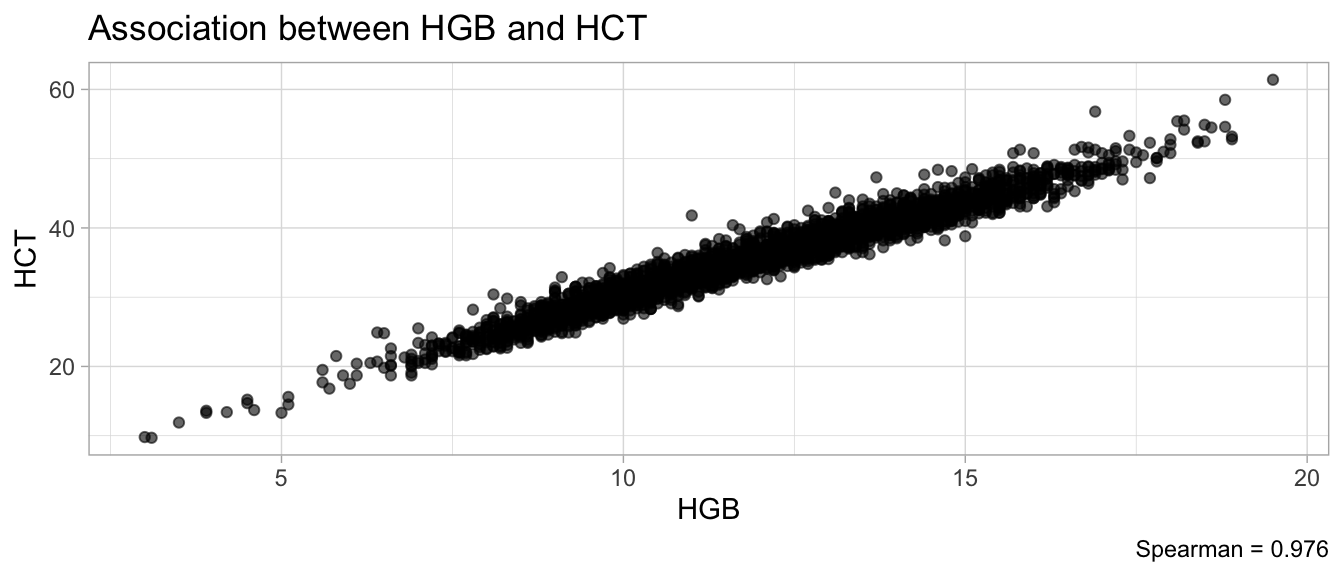
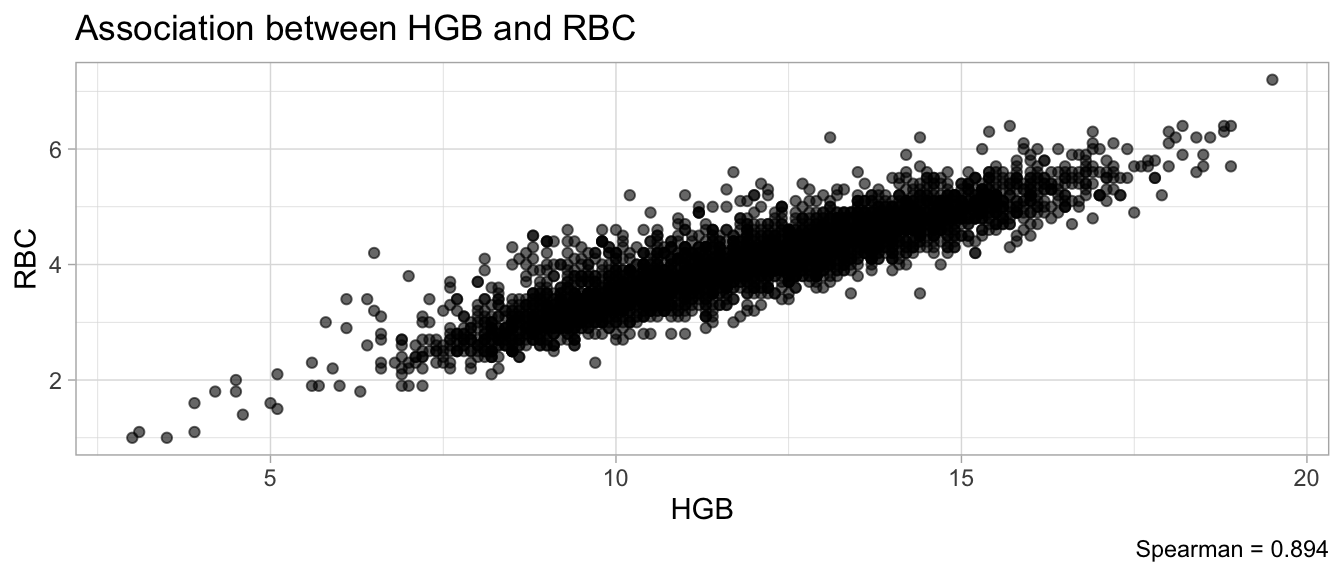
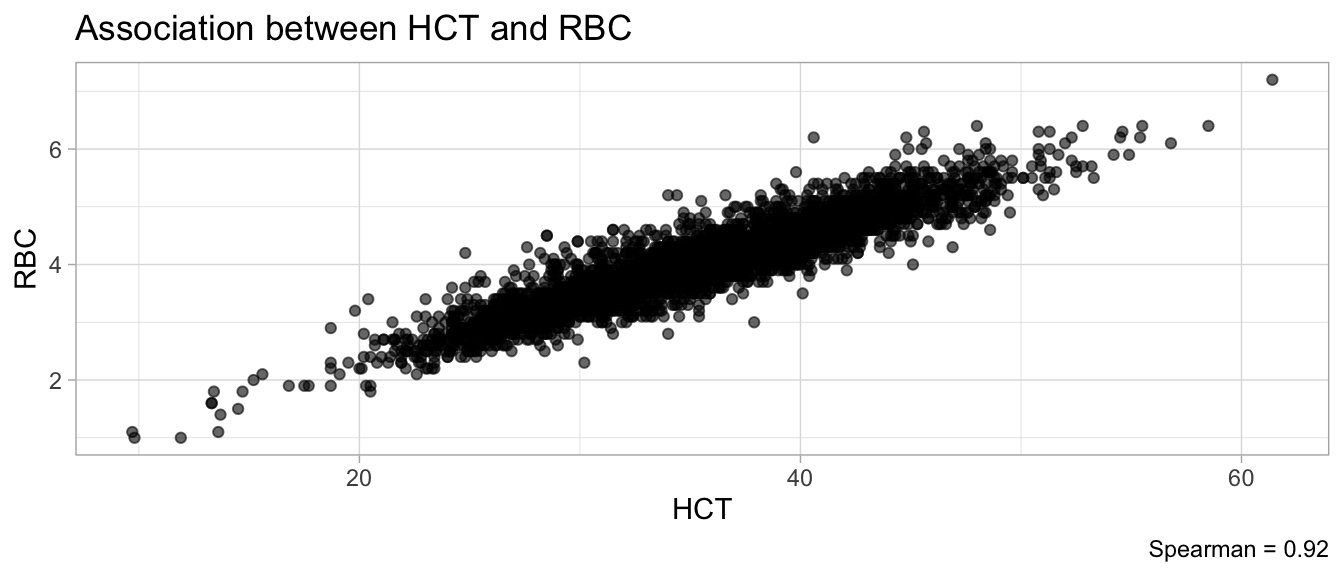
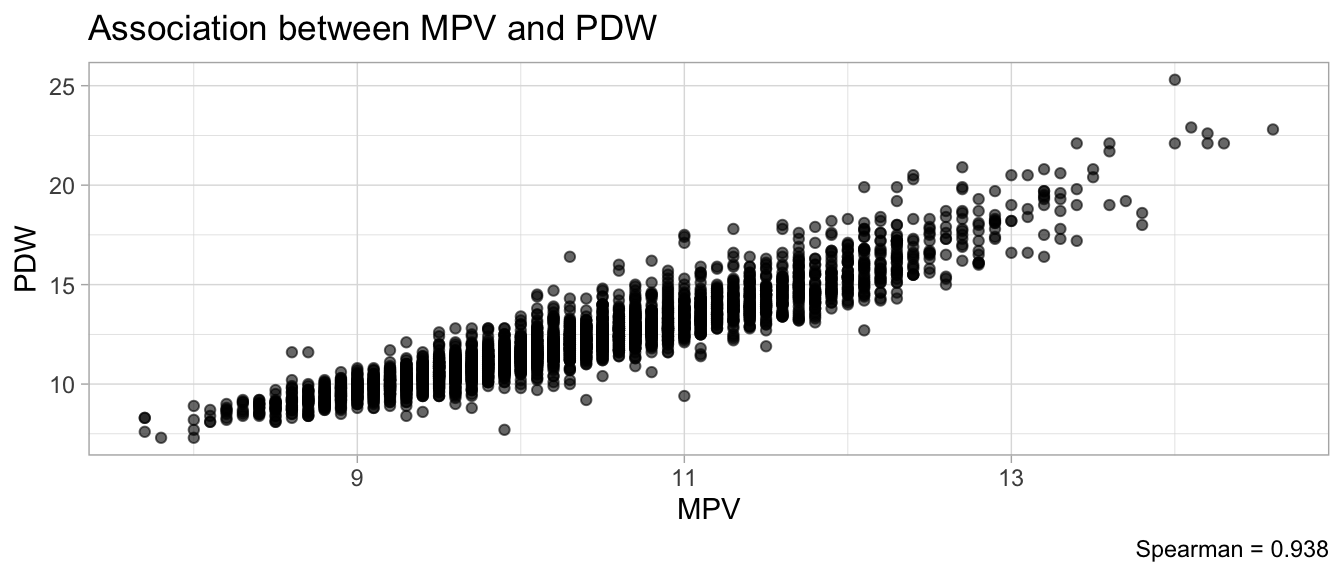
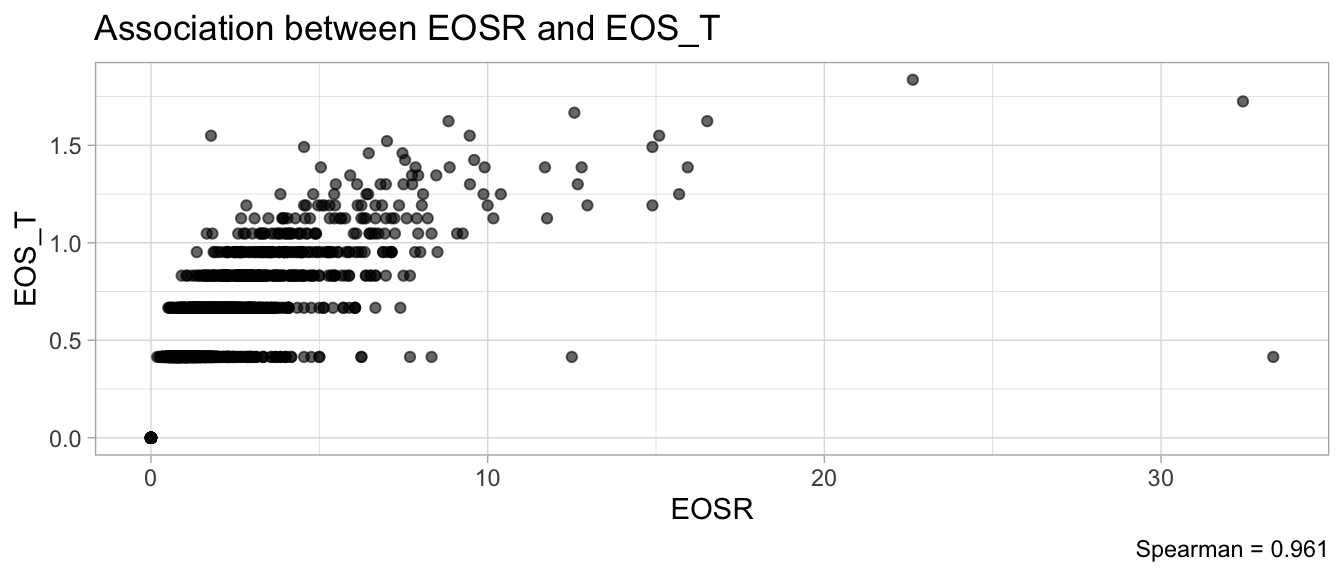
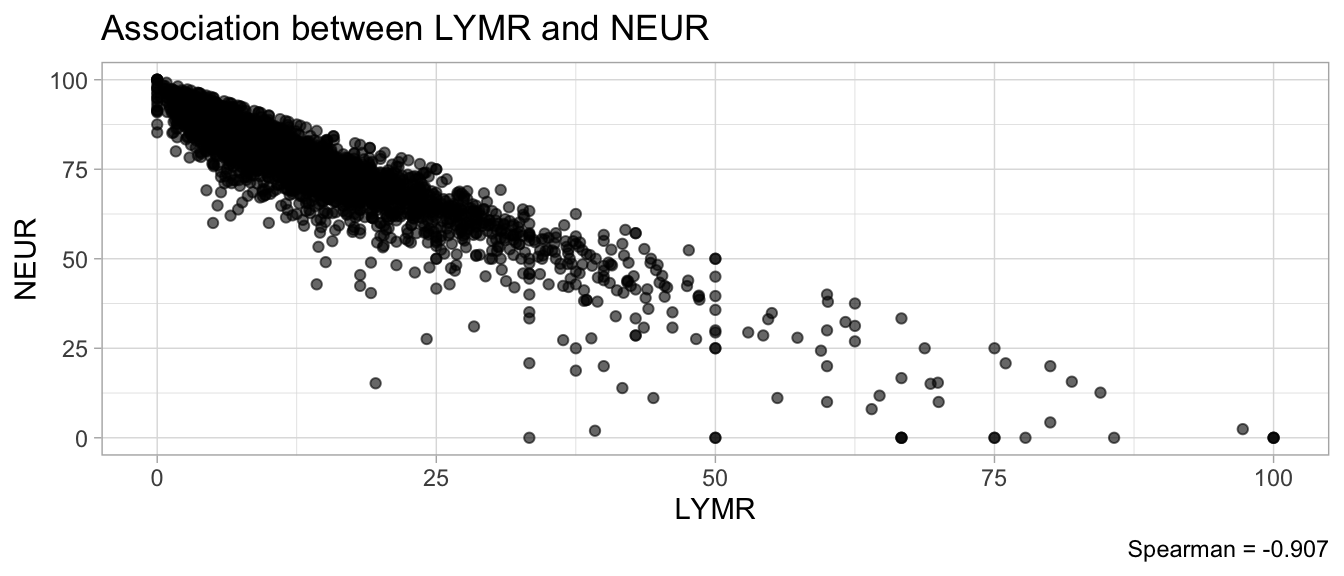
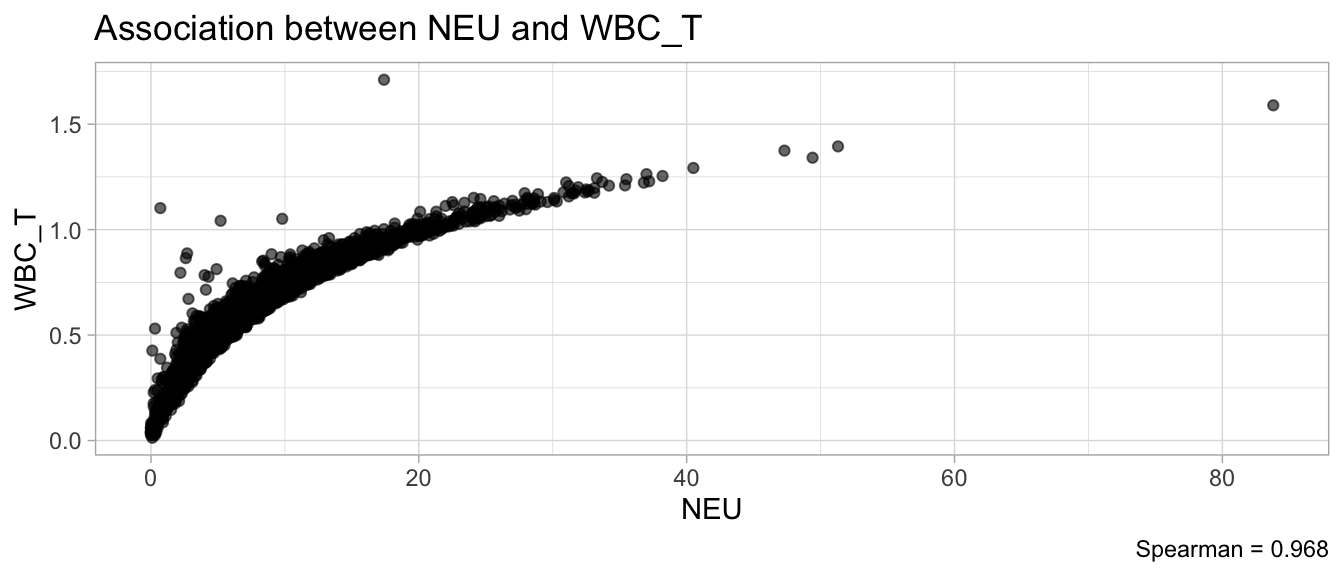
# Multivariate analyses `data/ADLB_02.rds` . ```{r, echo = FALSE, message = FALSE, warning = FALSE } library (tidyr)library (dplyr)library (ggplot2)library (purrr)library (tidyselect)library (corrr) ## tidy correlation library (patchwork)library (ggpubr)library (ggrepel)library (here)library (dendextend)library (gt)library (gtExtras)## for network plot options (ggrepel.max.overlaps = 100 )source (here ("R" , "fun_compare_dist_plot.R" ))source (here ("R" , "fun_compare_mult_dists.R" ))source (here ("R" , "fun_ida_trans.R" ))## Load the datasets - make sure to load the correct ADLB2 ## TODO : have a make workflow to ensure dependencies run in correct order <- readRDS (here:: here ("data" ,"IDA" , "ADSL_01.rds" ))<- readRDS (here:: here ("data" ,"IDA" , "ADLB_02.rds" ))``` ## V1: Association with structural variables ```{r mvi01, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} ## Join with ADSL for structural variables <- |> select (USUBJID, AGEGR01C, AGE, SEXC, SEX) <- ADLB |> left_join (ADSL01, by = "USUBJID" )``` ### Key predictors ```{r mvi03, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} #| layout-ncol: 2 ## plots for key predictors - remove age to avoid age vs age plot <- dat |> filter (! PARAMCD == "AGE" ) |> filter (KEY_PRED_FL02 == "Y" ) |> group_by (PARAMCD) |> group_map (~ plot_assoc_by (.x), .keep = TRUE )## print out. TODO : ask GH which plots to save for (plts in key_predictors) {print (plts)``` ### Predictors of medium importance ```{r mvi04, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} #| layout-ncol: 2 <- dat |> filter (MED_PRED_FL02 == "Y" ) |> group_by (PARAMCD) |> group_map (~ plot_assoc_by (.x), .keep = TRUE )for (plts in medium_predictors) {print (plts)``` ## V2: Correlation coefficients between all predictors ```{r mcorrs, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} ## tidy parameters in to a wide data set <- dat |> filter (KEY_PRED_FL02 == "Y" | MED_PRED_FL02 == "Y" | REM_PRED_FL02 == "Y" ) |> select (USUBJID, PARAMCD, AVAL, SEX) |> pivot_wider (names_from = PARAMCD, values_from = AVAL, values_fill = NA ) ## calculate corr matrix using spearman cc <- |> select (- USUBJID) |> correlate (use = "pairwise.complete.obs" ,method = "spearman" ,diagonal = NA )``` ```{r plotcorr, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.width = 16, fig.height=16} |> rearrange (method = "HC" ) |> autoplot (# method = "PCA", triangular = "lower" ,barheight = 20 ) + theme (axis.text.x = ggplot2:: element_text (angle = 45 , vjust = 1 , hjust = 1 , size = 8 ),axis.text.y = ggplot2:: element_text (vjust = 1 , hjust = 1 , size = 9 )``` ```{r} ## If we want to write to file or save # spearman_corr |> # shave(upper = TRUE) |> # fashion() |> # gt::gt() ``` ### VE1: Comparing nonparametric and parametric predictor correlation ```{r corr_setup, message = FALSE, warning = FALSE, echo = FALSE, fig.width = 16, fig.height=16} # differences of pearson and spearman correlations to check for outliers ## cast as a matrix <- |> as_matrix ()## calculate pearson cc <- |> select (- USUBJID) |> correlate (use = "pairwise.complete.obs" ,method = "pearson" ,diagonal = NA )## cast as matrix <- |> as_matrix ()## calculate the difference <- corr_spearman_mat - corr_pearson_mat## cast as tidy data frame TODO : could do this through a join? <- corrd |> as_cordf ()``` ```{r plotcorr_diff, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.width = 16, fig.height=16} ## plot |> rearrange (method = "HC" ) |> autoplot (# method = "PCA", triangular = "lower" ,barheight = 20 ) + theme (axis.text.x = ggplot2:: element_text (angle = 45 , vjust = 1 , hjust = 1 , size = 8 ),axis.text.y = ggplot2:: element_text (vjust = 1 , hjust = 1 , size = 9 )``` ```{r plotcorr02, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.width = 16, fig.height=16} # sparsified differences of correlation coefficients <- |> stretch () |> mutate (r = if_else (abs (r) > 0.1 , r, 0 )) |> retract () |> as_cordf ()## todo: remove zero entries? |> rearrange (method = "HC" ) |> autoplot (# method = "PCA", triangular = "lower" ,barheight = 20 ) + theme (axis.text.x = ggplot2:: element_text (angle = 45 , vjust = 1 , hjust = 1 , size = 8 ),axis.text.y = ggplot2:: element_text (vjust = 1 , hjust = 1 , size = 9 )``` ```{r plotcorr03, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.width = 12, fig.height=12} #corr_difference_conditional |> # shave() |> # rplot(print_cor = TRUE) #corrd_sp <- corrd #corrd_sp[abs(corrd)<0.1] <-0 #ggcorrplot(corrd_sp, tl.cex=5, tl.srt=90) #ggcorrplot(corrd_sp, type = "lower", outline.col = "white") ``` `r` ) is greater than 0.1. ```{r pred_corr, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE} ## COMMENT @Mark can we print pearson and spearman correlation coefficients into/over the graphs? <- |> shave () |> stretch () |> filter (r > 0.1 ) |> :: gt () |> :: fmt_number (columns = c (r),decimals = 2 |> :: gt_theme_538 ()``` ```{r ve3, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} #| layout-ncol: 3 ## Data prep <- combos |> mutate (grp = row_number ())<- |> stretch () |> rename (spearman = r)<- |> stretch () |> rename (pearson = r)<- combos01 |> left_join (combos_spearman) |> left_join (combos_pearson)``` ```{r ve3_02, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} #| layout-ncol: 3 ## Plot the data. source (here ("R" , "V2-mv-descriptions.R" ))<- |> group_by (grp) |> group_map (~ plot_scatter_corr (.x), .keep = TRUE )``` ```{r ve3_03, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} #| layout-ncol: 3 ## print out. TODO : ask GH which plots to save for (plts in combos3) {print (plts)``` ### VE2: Variable clustering ```{r varclust, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.width = 12, fig.height=12} source (here ("R" , "VE2-varclust.R" ))ve2_varclust (corr_spearman)#vc_bact<-Hmisc::varclus(as.matrix(dat)) #plot(vc_bact, cex=0.7, hang=0.01) ``` ```{r varclust02, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.width = 12, fig.height=8} #options(ggrepel.max.overlaps = 100) |> network_plot ()``` ```{r varclust03, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.width = 12, fig.height=6} # plot network with min cor of 0.3. # corr_spearman |> network_plot(min_cor = 0.3) ``` ```{r varclust04, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.width = 12, fig.height=6} <- |> shave () |> stretch () |> rename (spearman = r) |> filter (abs (spearman) > 0.8 ) |> mutate (grp = row_number ())``` ```{r varclust05, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} #| layout-ncol: 2 source (here ("R" , "V2-mv-descriptions.R" ))<- |> group_by (grp) |> group_map (~ plot_scatter_corr (.x, pearson_flag = FALSE ), .keep = TRUE )## print out. TODO : ask GH which plots to save for (plts in combos_spearman_03 ) {print (plts)``` ### VE3: Redundancy #### VIF for key predictor model ```{r vif, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} <- dat |> filter (KEY_PRED_FL02 == "Y" ) |> select (USUBJID, PARAMCD, AVAL, SEX) |> pivot_wider (names_from = PARAMCD, values_from = AVAL, values_fill = NA ) <- dat_wide |> select (- USUBJID)<- as.formula (paste (c ("~" ,paste (names (dat_vif), collapse= "+" )), collapse= "" ))#formula <- Hmisc:: redun (formula, data = dat_vif, nk= 0 , pr= FALSE )<- 1 / (1 - red$ rsq1)#cat("\nAvailable samvple size:\n", red$n, " (", #round(100*red$n/nrow(dat),2), "%)\n") <- as_tibble (vif, rownames = "PARAMCD" ) |> rename (vif = value)<- as_tibble (red$ rsq1, rownames = "PARAMCD" ) |> rename (r2 = value)<- vif_df |> left_join (red_df, by = "PARAMCD" )``` `r red$n` (`r round(100*red$n/nrow(dat),2)` %).```{r vif02, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} #vif_df |> gt::gt(caption = "Variance inflation factors") #red_df |> gt::gt(caption = "Multiple R-squared") |> gt () |> :: cols_label (PARAMCD = "Parameter code" ,r2 = "Multiple R-squared" ,vif = "Variance inflation factor" |> fmt_number (columns = c (r2),decimals = 2 |> fmt_number (columns = c (vif),decimals = 1 |> gt_theme_538 ()``` #### VIF for model with key predictors and predictors of medium importance ```{r vif03, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} <- dat |> filter (KEY_PRED_FL02 == "Y" | MED_PRED_FL02 == "Y" ) |> select (USUBJID, PARAMCD, AVAL, SEX) |> pivot_wider (names_from = PARAMCD, values_from = AVAL, values_fill = NA ) <- dat_wide |> select (- USUBJID)<- as.formula (paste (c ("~" ,paste (names (dat_vif), collapse= "+" )), collapse= "" ))#formula <- Hmisc:: redun (formula, data = dat_vif, nk= 0 , pr= FALSE )<- 1 / (1 - red$ rsq1)#cat("\nAvailable samvple size:\n", red$n, " (", #round(100*red$n/nrow(dat),2), "%)\n") <- as_tibble (vif, rownames = "PARAMCD" ) |> rename (vif = value)<- as_tibble (red$ rsq1, rownames = "PARAMCD" ) |> rename (r2 = value)<- vif_df |> left_join (red_df, by = "PARAMCD" )``` `r red$n` (`r round(100*red$n/nrow(dat),2)` %).```{r vif04, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} #vif_df |> gt::gt(caption = "Variance inflation factors") #red_df |> gt::gt(caption = "Multiple R-squared") |> gt () |> :: cols_label (PARAMCD = "Parameter code" ,r2 = "Multiple R-squared" ,vif = "Variance inflation factor" |> fmt_number (columns = c (r2),decimals = 2 |> fmt_number (columns = c (vif),decimals = 1 |> gt_theme_538 ()``` #### VIF for all predictor model #### Redundancy by parametric additive model: key predictor model ```{r key_vif, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} <- dat |> filter (KEY_PRED_FL02 == "Y" ) |> select (USUBJID, PARAMCD, AVAL, SEX) |> pivot_wider (names_from = PARAMCD, values_from = AVAL, values_fill = NA ) <- dat_wide |> select (- USUBJID)<- as.formula (paste (c ("~" ,paste (names (dat_vif), collapse= "+" )), collapse= "" ))<- Hmisc:: redun (formula, data = dat_vif, pr= FALSE )<- 1 / (1 - red$ rsq1)#cat("\nAvailable samvple size:\n", red$n, " (", #round(100*red$n/nrow(dat),2), "%)\n") <- as_tibble (vif, rownames = "PARAMCD" ) |> rename (vif = value)<- as_tibble (red$ rsq1, rownames = "PARAMCD" ) |> rename (r2 = value)<- vif_df |> left_join (red_df, by = "PARAMCD" )``` `r red$n` (`r round(100*red$n/nrow(dat),2)` %).```{r key_vif02, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} #vif_df |> gt::gt(caption = "Variance inflation factors") #red_df |> gt::gt(caption = "Multiple R-squared") |> gt () |> :: cols_label (PARAMCD = "Parameter code" ,r2 = "Multiple R-squared" ,vif = "Variance inflation factor" |> fmt_number (columns = c (r2),decimals = 2 |> fmt_number (columns = c (vif),decimals = 1 |> gt_theme_538 ()``` #### Redundancy by parametric additive model: key predictors and predictors of medium importance ```{r key_vif03, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} <- dat |> filter (KEY_PRED_FL02 == "Y" | MED_PRED_FL02 == "Y" ) |> select (USUBJID, PARAMCD, AVAL, SEX) |> pivot_wider (names_from = PARAMCD, values_from = AVAL, values_fill = NA ) <- dat_wide |> select (- USUBJID)<- as.formula (paste (c ("~" ,paste (names (dat_vif), collapse= "+" )), collapse= "" ))#formula <- Hmisc:: redun (formula, data = dat_vif, pr= FALSE )<- 1 / (1 - red$ rsq1)#cat("\nAvailable samvple size:\n", red$n, " (", #round(100*red$n/nrow(dat),2), "%)\n") <- as_tibble (vif, rownames = "PARAMCD" ) |> rename (vif = value)<- as_tibble (red$ rsq1, rownames = "PARAMCD" ) |> rename (r2 = value)<- vif_df |> left_join (red_df, by = "PARAMCD" )``` `r red$n` (`r round(100*red$n/nrow(dat),2)` %).```{r key_vif04, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.height=3} #vif_df |> gt::gt(caption = "Variance inflation factors") #red_df |> gt::gt(caption = "Multiple R-squared") |> gt () |> :: cols_label (PARAMCD = "Parameter code" ,r2 = "Multiple R-squared" ,vif = "Variance inflation factor" |> fmt_number (columns = c (r2),decimals = 2 |> fmt_number (columns = c (vif),decimals = 1 |> gt_theme_538 ()```